The Rise of Electric Vehicles: Driving Toward a Sustainable Future
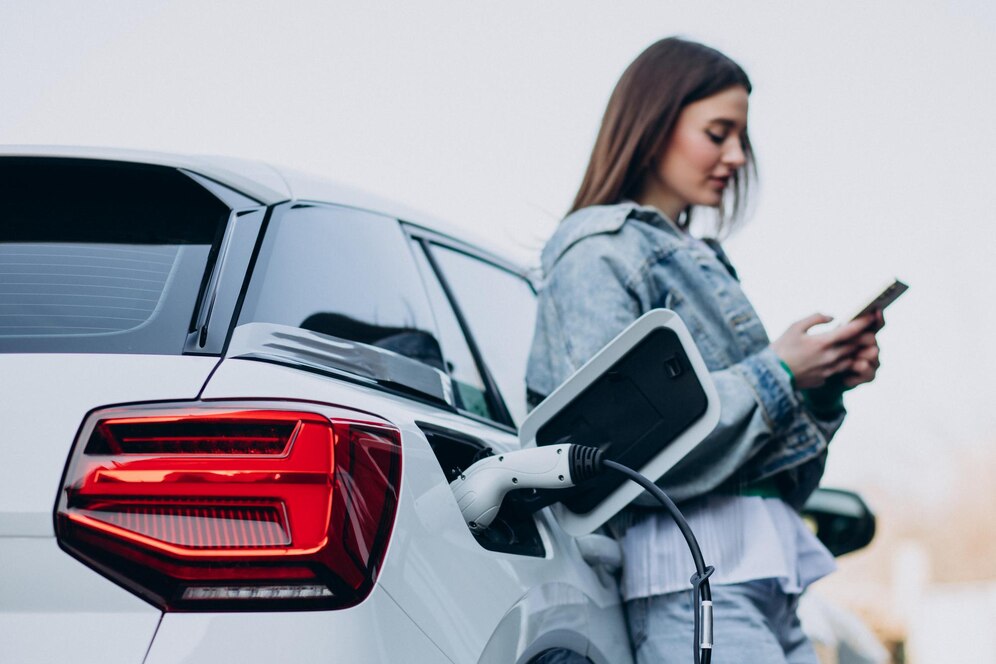
Electric vehicles (EVs) have moved from futuristic novelties to mainstream transportation options in just a few short decades. Today, they represent the vanguard of a global effort to decarbonize transportation, reduce air pollution, and reimagine the way we power our mobility. As concerns over climate change, energy security, and urban air quality intensify, EVs are no longer just an eco-conscious choice—they’re quickly becoming the smart one. In this blog, we’ll explore the evolution of electric vehicles, their environmental and economic benefits, the challenges they face, and what the future might hold for this fast-growing sector. The Evolution of Electric Vehicles Although EVs may seem like a modern innovation, they’ve been around longer than most people realize. The first electric cars appeared in the late 19th century and were actually more popular than gasoline-powered cars in the early 1900s. They were quieter, easier to operate, and didn’t require a hand crank to start. However, the discovery of vast petroleum reserves, the development of internal combustion engines, and the mass production of cars like the Ford Model T eventually led to the dominance of gasoline vehicles. The interest in EVs resurfaced in the late 20th century, driven by environmental concerns and advances in battery technology. However, limited range, high costs, and a lack of infrastructure kept adoption low. That began to change in the 2010s with the launch of models like the Nissan Leaf and the Tesla Model S, which offered improved range, performance, and desirability. Why the Shift Toward EVs? 1. Environmental Benefits Perhaps the most compelling reason for the shift to electric vehicles is their environmental advantage. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they don’t release harmful gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), or particulate matter while driving. These pollutants are major contributors to air pollution, respiratory illnesses, and global warming. Furthermore, when EVs are powered by renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power, their lifecycle emissions are significantly lower than those of gasoline or diesel vehicles. Even when charged using electricity from fossil fuel-heavy grids, EVs generally outperform traditional vehicles in terms of carbon emissions. 2. Energy Efficiency Electric motors are far more efficient than internal combustion engines. While a typical gasoline engine converts only about 20–30% of the energy from fuel into motion, electric motors can convert over 85% of electrical energy into movement. This efficiency translates to lower energy use and cost per kilometer driven. 3. Lower Operating Costs Over the long term, EVs can be significantly cheaper to own and operate. Electricity is often cheaper than gasoline or diesel on a per-mile basis. Maintenance costs are also lower because EVs have fewer moving parts and don’t require oil changes, exhaust system repairs, or timing belt replacements. 4. Innovation and Performance Today’s electric vehicles are not just practical—they’re exciting. EVs offer instant torque, providing quick acceleration and a responsive driving experience. Tesla’s high-performance models, for example, can rival or even surpass some of the fastest gas-powered sports cars. Additionally, modern EVs come equipped with cutting-edge technology, including autonomous driving features, regenerative braking, and seamless software updates. Current Challenges Facing EV Adoption Despite the clear advantages, several challenges continue to slow down widespread EV adoption: 1. Charging Infrastructure While urban areas in many developed countries are beginning to see a proliferation of charging stations, rural areas and less affluent regions still face a dearth of charging options. Fast-charging stations can be expensive to install, and the charging process still takes significantly longer than filling up a gas tank. 2. Range Anxiety Although newer EV models boast ranges of 300 miles (480 kilometers) or more, range anxiety—the fear of running out of battery before reaching a charging station—remains a psychological barrier for many potential buyers. This concern is especially significant in regions with limited charging infrastructure. 3. Battery Costs and Sustainability Batteries are one of the most expensive components of an electric vehicle. Although prices have fallen dramatically in the past decade, they still contribute significantly to the overall cost of EVs. Moreover, the production of lithium-ion batteries raises concerns over the mining of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which have environmental and ethical implications. 4. Grid Demand As more EVs are adopted, electricity grids will face increased demand. This shift necessitates smarter grid management, energy storage solutions, and greater reliance on renewable energy sources to ensure that EVs truly contribute to a cleaner environment. Government Policies and Industry Commitments Recognizing the benefits of EVs, many governments around the world are enacting policies to accelerate their adoption. These include: At the same time, automakers are rising to the challenge. Companies like General Motors, Ford, Volkswagen, and Toyota have announced multi-billion-dollar investments in EV production. Tesla, Rivian, BYD, and other startups are also pushing innovation in the sector. The Future of Electric Mobility Looking ahead, the future of electric vehicles appears bright. Battery technology is evolving rapidly, promising faster charging times, longer ranges, and improved durability. Emerging technologies such as solid-state batteries, wireless charging, and vehicle-to-grid integration could further revolutionize how we use and power our cars. In addition, the concept of mobility is itself changing. With the rise of ride-sharing, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, EVs will play a crucial role in the next generation of transportation systems. They offer a path not just to cleaner cars, but to a cleaner, smarter, and more connected world. Conclusion Electric vehicles are more than just a trend—they are a cornerstone of the global effort to build a sustainable future. While challenges remain, the momentum behind EVs is undeniable. With continued innovation, supportive policies, and public engagement, electric vehicles have the potential to reshape our roads, our cities, and our planet for the better.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles: Driving Toward a Sustainable Future Read More »